Elasticsearch query
editElasticsearch query
editThe Elasticsearch query rule type runs a user-configured query, compares the number of matches to a configured threshold, and schedules actions to run when the threshold condition is met.
Create the rule
editFill in the rule details, then select Elasticsearch query.
Define the conditions
editDefine properties to detect the condition.
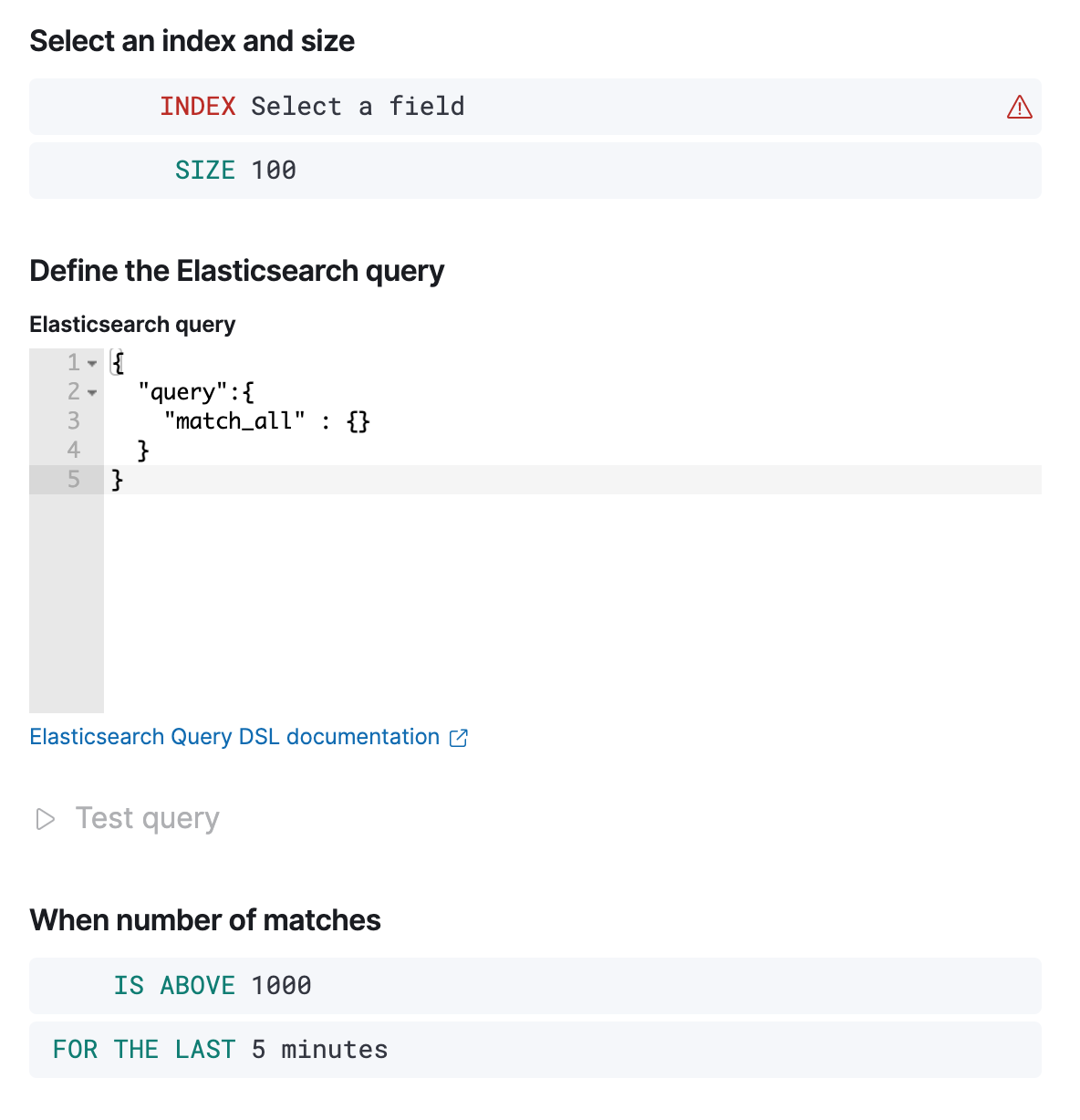
- Index
- Specifies an index or data view and a time field that is used for the time window.
- Size
- Specifies the number of documents to pass to the configured actions when the threshold condition is met.
- Elasticsearch query
-
Specifies the ES DSL query. The number of documents that
match this query is evaluated against the threshold condition. Only the
queryfield is used, other DSL fields are not considered. - Threshold
-
Defines a threshold value and a comparison operator (
is above,is above or equals,is below,is below or equals, oris between). The number of documents that match the specified query is compared to this threshold. - Time window
- Defines how far back to search for documents, using the time field set in the index clause. Generally this value should be set to a value higher than the check every value in the general rule details, to avoid gaps in detection.
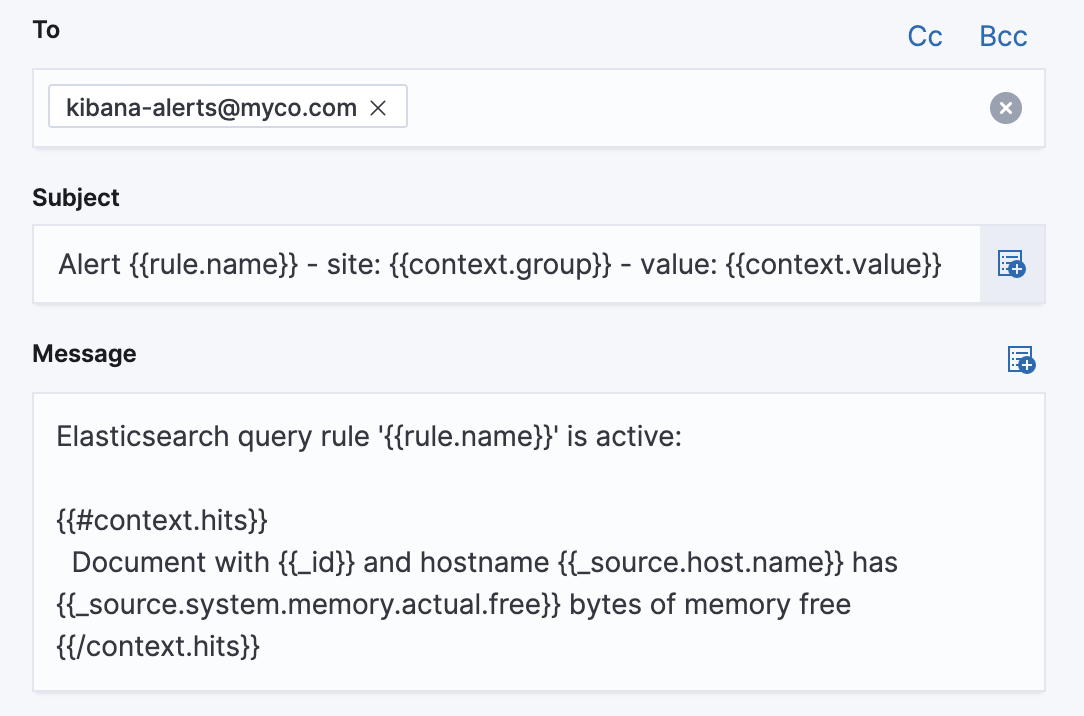
Add action variables
editAdd an action to run when the rule condition is met. The following variables are specific to the Elasticsearch query rule. You can also specify variables common to all rules.
-
context.title -
A preconstructed title for the rule. Example:
rule term match alert query matched. -
context.message -
A preconstructed message for the rule. Example:
rule 'my es-query' is active:
- Value: 2
- Conditions Met: Number of matching documents is greater than 1 over 5m
- Timestamp: 2022-02-03T20:29:27.732Z -
context.group -
The name of the action group associated with the condition.
Example:
query matched. -
context.date -
The date, in ISO format, that the rule met the condition.
Example:
2022-02-03T20:29:27.732Z. -
context.value - The value of the rule that met the condition.
-
context.conditions -
A description of the condition. Example:
count greater than 4. -
context.hits -
The most recent documents that matched the query. Using the Mustache template array syntax, you can iterate over these hits to get values from the ES documents into your actions.
Test your query
editUse the Test query feature to verify that your query DSL is valid.
-
Valid queries are run against the configured index using the configured time window. The number of documents that match the query is displayed.

-
An error message is shown if the query is invalid.

Handling multiple matches of the same document
editThis rule type checks for duplication of document matches across multiple runs. If you configure the rule with a schedule interval smaller than the time window, and a document matches a query in multiple runs, it is alerted on only once.
The rule uses the timestamp of the matches to avoid alerting on the same match multiple times. The timestamp of the latest match is used for evaluating the rule conditions when the rule runs. Only matches between the latest timestamp from the previous run and the current run are considered.
Suppose you have a rule configured to run every minute. The rule uses a time window of 1 hour and checks if there are more than 99 matches for the query. The Elasticsearch query rule type does the following:
|
Rule finds 113 matches in the last hour: |
Rule is active and user is alerted. |
|
Rule finds 127 matches in the last hour. 105 of the matches are duplicates that were already alerted on previously, so you actually have 22 matches: |
No alert. |
|
Rule finds 159 matches in the last hour. 88 of the matches are duplicates that were already alerted on previously, so you actually have 71 matches: |
No alert. |
|
Rule finds 190 matches in the last hour. 71 of them are duplicates that were already alerted on previously, so you actually have 119 matches: |
Rule is active and user is alerted. |