Webhook connector and action
editWebhook connector and action
editThe Webhook connector uses axios to send a POST or PUT request to a web service.
Create connectors in Kibana
editYou can create connectors in Stack Management > Connectors or as needed when you’re creating a rule. For example:
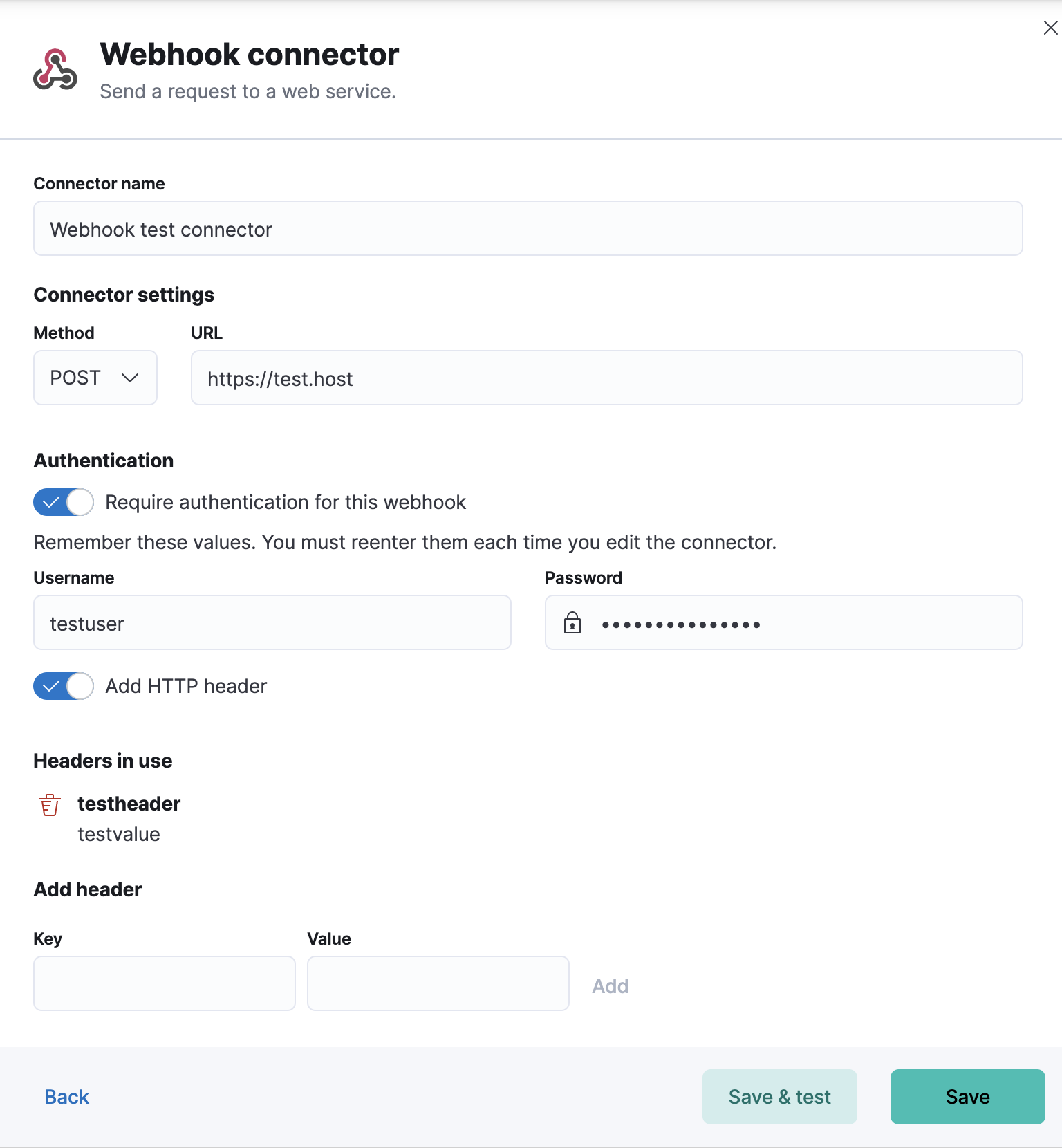
Connector configuration
editWebhook connectors have the following configuration properties:
- Name
- The name of the connector.
- URL
-
The request URL. If you are using the
xpack.actions.allowedHostssetting, make sure the hostname is added to the allowed hosts. - Method
-
HTTP request method, either
post(default) orput. - Headers
- A set of key-value pairs sent as headers with the request
- Require authentication
- If true, a username and password for login type authentication must be provided.
- Username
- Username for HTTP basic authentication.
- Password
- Password for HTTP basic authentication.
Create preconfigured connectors
editIf you are running Kibana on-prem, you can define connectors by
adding xpack.actions.preconfigured settings to your kibana.yml file.
For example:
xpack.actions.preconfigured:
my-webhook:
name: preconfigured-webhook-connector-type
actionTypeId: .webhook
config:
url: https://test.host
method: post
headers:
testheader: testvalue
secrets:
user: testuser
password: passwordkeystorevalue
Config defines information for the connector type.
-
url - A URL string that corresponds to URL.
-
method - A string that corresponds to Method.
-
headers - A record<string, string> that corresponds to Headers.
-
hasAuth -
A boolean that corresponds to Requires authentication. If
true, this connector will require values foruserandpasswordinside the secrets configuration. Defaults totrue.
Secrets defines sensitive information for the connector type.
-
user -
A string that corresponds to User. Required if
hasAuthis set totrue. -
password -
A string that corresponds to Password. Should be stored in the Kibana keystore. Required if
hasAuthis set totrue.
Test connectors
editYou can test connectors with the run connector API or as you’re creating or editing the connector in Kibana. For example:
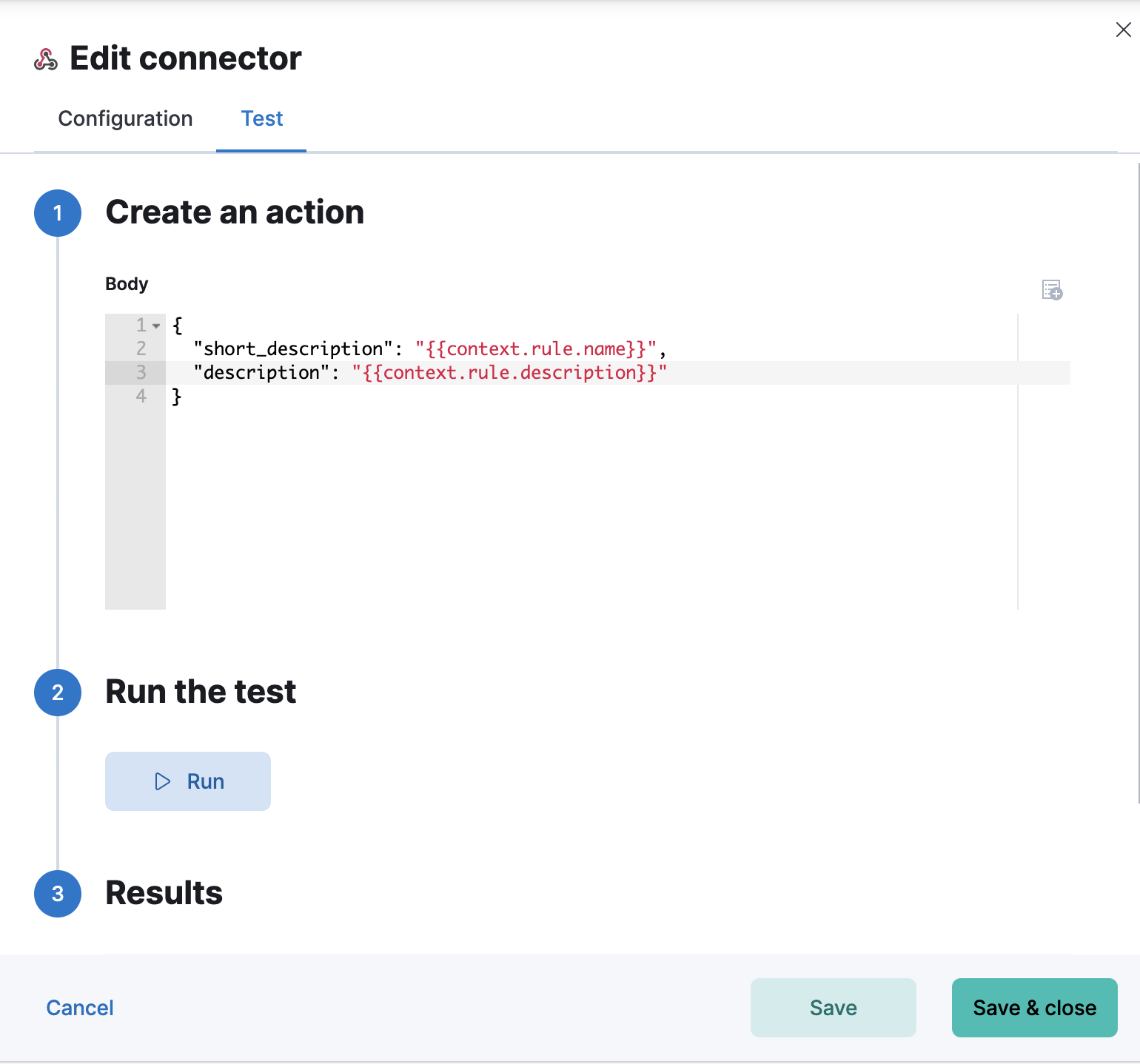
Webhook actions have the following properties.
- Body
-
A JSON payload sent to the request URL. For example:
{ "short_description": "{{context.rule.name}}", "description": "{{context.rule.description}}", ... }
Mustache template variables (the text enclosed in double braces, for example, context.rule.name) have
their values escaped, so that the final JSON will be valid (escaping double quote characters).
For more information on Mustache template variables, refer to Actions.
Connector networking configuration
editUse the Action configuration settings to customize connector networking configurations, such as proxies, certificates, or TLS settings. You can set configurations that apply to all your connectors or use xpack.actions.customHostSettings to set per-host configurations.