It is time to say goodbye: This version of Elastic Cloud Enterprise has reached end-of-life (EOL) and is no longer supported.
The documentation for this version is no longer being maintained. If you are running this version, we strongly advise you to upgrade. For the latest information, see the current release documentation.
Architecture
editArchitecture
editECE shares most of its codebase with Elastic Cloud. The key tenets of the architecture are:
- Service-oriented architecture
- Containerization using Docker
- Deployment state coordination using ZooKeeper
- Easy access through the Cloud UI
Service-oriented architecture
editAn ECE installation consists of a number of core services. This service-oriented architecture lets you:
- Scale the platform easily. Different services can have different reliability and performance requirements, as each service can be scaled separately.
- Access services via API, easing operational management and enabling changes and improvements to one service without affecting all the other services.
- Deploy each service independently in its own Docker container. Combined with fine-grained permissions to read and write application state, your whole installation is more secure. Even if a service is compromised, the damage is contained within a single container plus part of the application state.
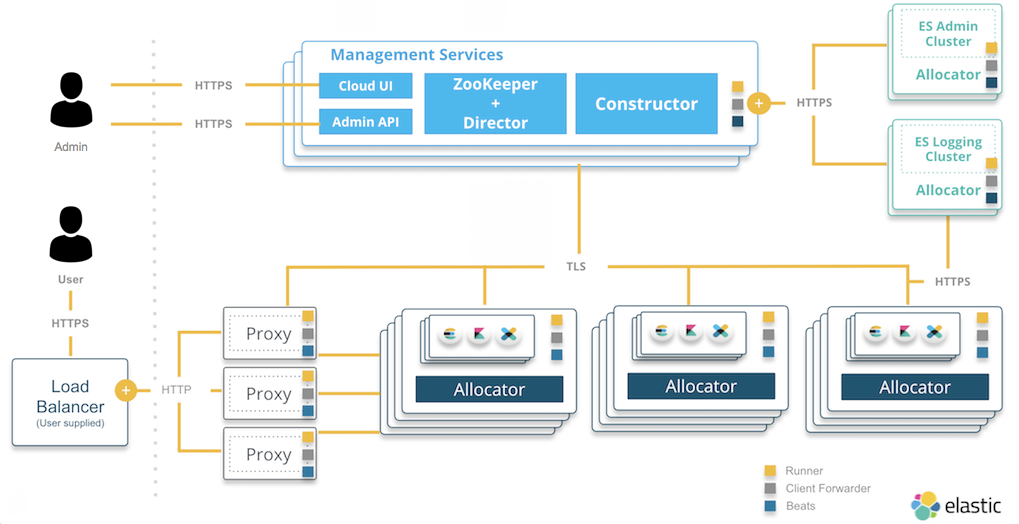
Proxies
Proxies handle user requests, mapping deployment IDs that are passed in request URLs for the container to the actual Elasticsearch cluster nodes and other instances. The association of deployment IDs to a container is stored in ZooKeeper, cached by the proxies. In the event of ZooKeeper downtime, the platform can still service the requests to existing deployments by using the cache.
Proxies are intelligent: if you have a highly available Elasticsearch cluster, so that your nodes are spread across two or three availability zones, proxies keep track of the state and availability of zones. If one of the zones goes down, then the proxy handling your user request will not route any requests there.
Proxies help with no-downtime scaling and upgrades. Before performing an upgrade, a snapshot is taken, and then new nodes with a new configuration or a new quota are spun up. The data is migrated to the new nodes using standard Elasticsearch features. When the migration is complete, a proxy switches the traffic to the new nodes and disconnects the old ones.
Note that you should put your own load balancer in front the proxies to make sure that the system remains available, even if one of the proxies goes down.
Allocators
Allocators let you scale the ECE installation. They run on all the machines that you want to host Elasticsearch nodes and Kibana instances on. Containers with Elasticsearch cluster nodes are then run on the machines managed by allocators.
Allocators advertise the resources of the underlying host machine in ZooKeeper. They control the lifecycle of cluster nodes by:
- Creating new containers and starting Elasticsearch nodes when requested
- Restarting a node if it becomes unresponsive
- Removing a node if it is no longer needed
Using Docker containers guarantees shares of resources for the underlying deployments, which mitigates the noisy neighbor effect where one busy deployment can overwhelm the entire host. The CPU resources that get assigned to an Elasticsearch cluster are relative to the size of a cluster, so that larger clusters get assigned a larger share of CPU resources than smaller ones. For example, a cluster with 32GB of RAM gets assigned twice as many CPU resources as a cluster with 16GB of RAM.
Management services
Sometimes also referred to as the control plane of ECE, these services control include several core components of ECE:
-
Constructors: Provide the requests that allocators respond to when they manage containers and Elasticsearch nodes. Each constructor monitors new requests from the administration console, which supports the Cloud UI and the RESTful API that you use to manage ECE, determines what needs to be changed, and writes the changes to ZooKeeper nodes monitored by the allocators. Constructors also assign cluster nodes to allocators.
If you select a deployment plan with high availability, the constructor will place cluster nodes and instances within different availability zones to ensure that the deployment can survive any downtime of a whole zone. You can designate these availability zones when you install ECE. Additionally, the constructor maximizes the utilization of underlying allocators to reduce the need to spin up extra hardware for new deployments.
-
ZooKeeper and directors: ZooKeeper coordinates the state of Elastic Cloud Enterprise and the state of all deployments running in your installation. Within ECE, ZooKeeper is managed by directors.
Directors sign the CSRs (certificate signing requests) for internal clients that want to communicate with ZooKeeper. They also maintain the stunnels used by ZooKeeper for communication, and they are involved in establishing quorum when new ZooKeeper nodes are created.
- Cloud UI and API: Provides web and API access to administrative functions for Elastic Cloud Enterprise.. Underneath, the administration console provides the necessary support for both the Cloud UI and the API.
Containerization using Docker
editServices are deployed as Docker containers, which simplifies the operational effort and makes it easy to provision similar environments for development and staging. Each cluster node is run within a Docker container to make sure that all of the nodes have access to a guaranteed share of host resources.
Containerization also improves security. On the assumption that any cluster can be compromised, containers are given no access to the platform. The same is true for the services: each service can read or write only those parts of the system state that are relevant to it. Even if some services are compromised, the attacker won’t get hold of the keys to the rest of them and will not compromise the whole platform.
Stunnel
Docker containers communicate securely with one another using stunnel (rather than Transport Layer Security, which not all services or components support natively). Tunneling all traffic between containers makes sure that it is not possible to eavesdrop, even when someone else has access to the underlying cloud or network infrastructure.
Deployment state coordination using ZooKeeper
editZooKeeper stores the state of the ECE installation and the state of all deployments running in ECE. ZooKeeper is also the event bus coordinating all the other services.
ZooKeeper is a distributed, strongly consistent data store. It offers a file system-like structure, where each node is both a folder with subordinate items and a file that holds data. These nodes are called znodes to differentiate them from the physical nodes that ZooKeeper runs on.
ZooKeeper is designed to remain consistent even in the event of network partitions: a write operation is rejected unless it can be confirmed by a majority of ZooKeeper servers, and write operations are linear. You can set watches on znodes so that ZooKeeper can serve as an event bus where one service can notify another by writing to an observed znode. Znodes can have associated access control lists (ACLs) which provide fine-grained access to the system state for various services. For example, the constructor can write deployment plans, but allocators can only read them.
Easy access for admins through the Cloud UI and API
editThe Cloud user interface provides web-based access for administrators to manage and monitor your ECE installation. Many of the functions provided by the Cloud UI are also available through the API.
Examples of tasks you can perform from the Cloud UI and the API include:
- Administering installation-wide settings, working with runners (hosts you have installed ECE on), and configuring your deployment.
- Monitoring your ECE installation using Filebeat and Metric beat data.
- Creating and working with Elasticsearch clusters and Kibana.
As a companion piece to the Cloud UI, we also provide an API that supports many of the same functions. To learn more about the API, see our API Reference.