Extract fields
Serverless Stack
After selecting a stream, use the Processing tab to add processors that extract meaningful fields from your log messages. These fields let you filter and analyze your data more effectively.
For example, in Discover, extracted fields might let you filter for log messages with an ERROR log level that occurred during a specific time period to help diagnose an issue. Without extracting the log level and timestamp fields from your messages, those filters wouldn't return meaningful results.
The Processing tab also:
- Simulates your processors and provides an immediate preview that's tested end to end
- Flags indexing issues, like mapping conflicts, so you can address them before applying changes
After creating your processor, all future data ingested into the stream is parsed into structured fields accordingly.
Applied changes aren't retroactive and only affect future ingested data.
Streams supports the following processors:
- Date: Converts date strings into timestamps, with options for timezone, locale, and output formatting.
- Dissect: Extracts fields from structured log messages using defined delimiters instead of patterns, making it faster than Grok and ideal for consistently formatted logs.
- Grok: Extracts fields from unstructured log messages using predefined or custom patterns, supports multiple match attempts in sequence, and can automatically generate patterns with an LLM connector.
- Set: Assigns a specific value to a field, creating the field if it doesn’t exist or overwriting its value if it does.
- Rename: Changes the name of a field, moving its value to a new field name and removing the original.
- Append: Adds a value to an existing array field, or creates the field as an array if it doesn’t exist.
Streams uses Elasticsearch ingest pipelines made up of processors to transform your data, without requiring you to switch interfaces and manually update pipelines.
To add a processor from the Processing tab:
- Select Create → Create processor to open a list of supported processors.
- Select a processor from the Processor menu.
- Configure the processor and select Create to save the processor.
After adding all desired processors and conditions, select Save changes.
Refer to individual supported processors for more on configuring specific processors.
Editing processors with JSON is planned for a future release, and additional processors may be supported over time.
You can add conditions to processors so they only run on data that meets those conditions. Each condition is a boolean expression that's evaluated for every document.
To add a condition:
- Select Create → Create condition.
- Provide a Field, a Value, and a comparator.
- Select Create condition.
- Select Save changes.
Supported comparators
Streams processors support the following comparators:
- equals
- not equals
- less than
- less than or equals
- greater than
- greater than or equals
- contains
- starts with
- ends with
- exists
- not exists
After you create processors, the Data preview tab simulates processor results with additional filtering options depending on the outcome of the simulation.
When you add or edit processors, the Data preview tab updates automatically.
To avoid unexpected results, it's best to add processors rather than remove or reorder existing ones.
The Data preview tab loads 100 documents from your existing data and runs your changes against them. For any newly created processors and conditions, the preview results are reliable, and you can freely create and reorder during the preview.
After making sure everything in the Data preview tab is correct, select Save changes to apply your changes to the data stream.
If you edit the stream after saving your changes, keep the following in mind:
- Adding processors to the end of the list will work as expected.
- Editing or reordering existing processors can cause inaccurate results. Because the pipeline may have already processed the documents used for sampling, Data preview cannot accurately simulate changes to existing data.
- Adding a new processor and moving it before an existing processor may cause inaccurate results. Data preview only simulates the new processor, not the existing ones, so the simulation may not accurately reflect changes to existing data.
Each processor has the Ignore failures option. When enabled, document processing continues when even if the processor fails.
Dissect, grok, and rename processors include the Ignore missing fields option. When enabled, document processing continues even if a source field is missing.
Documents can fail processing for various reasons. Streams helps you identify and resolve these issues before deploying changes.
In the following screenshot, the Failed percentage indicates that some messages didn't match the provided grok pattern:
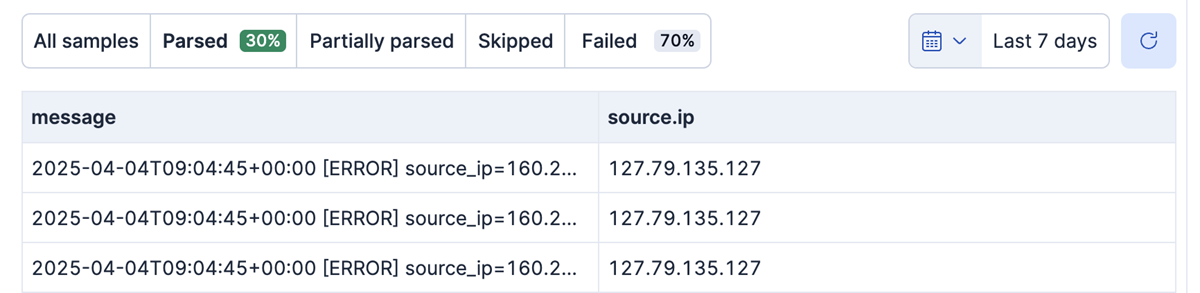
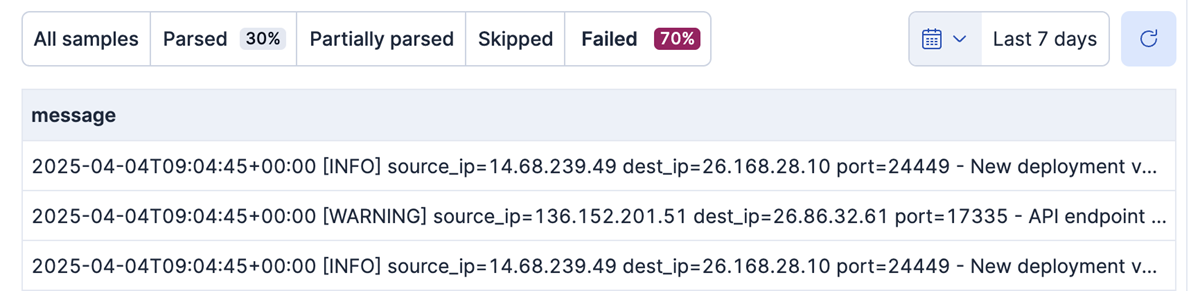
You can filter your documents by selecting Parsed or Failed on the Data preview tab. Selecting Failed shows the documents that weren't parsed correctly:
Failures are displayed at the bottom of the process editor. Some failures may require fixes, while others simply serve as a warning:
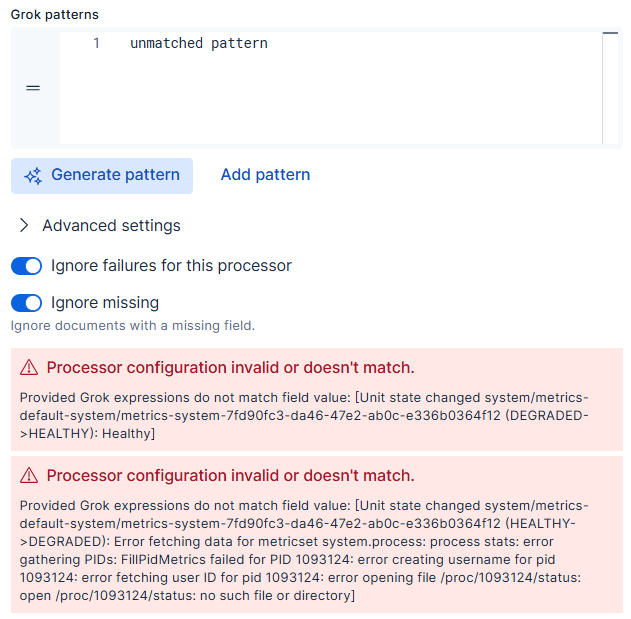
As part of processing, Streams simulates your changes end to end to check for mapping conflicts. If it detects a conflict, Streams marks the processor as failed and displays a message like the following:

Use the information in the failure message to find and troubleshoot the mapping issues.
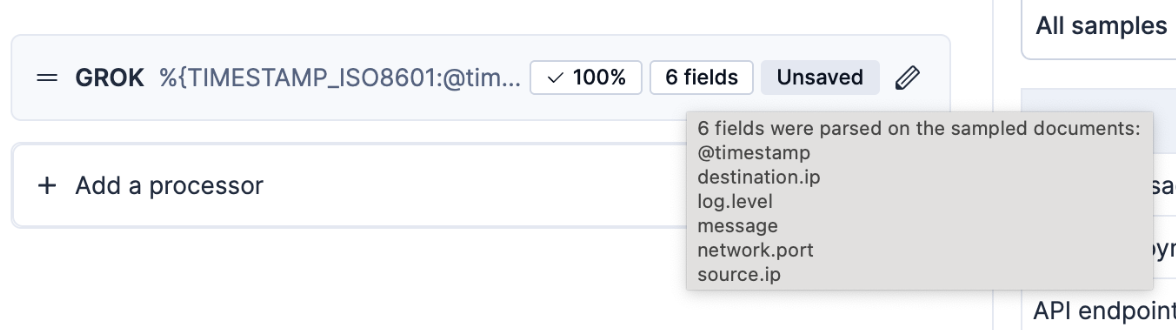
Once saved, the processor displays its success rate and the fields it added.
When you save processors, Streams appends processing to the best-matching ingest pipeline for the data stream. It either chooses the best-matching pipeline ending in @custom in your data stream, or it adds one for you.
Streams identifies the appropriate @custom pipeline (for example, logs-myintegration@custom or logs@custom) by checking the default_pipeline that is set on the data stream. You can view the default pipeline on the Advanced tab under Ingest pipeline.
In this default pipeline, Streams locates the last processor that calls a pipeline ending in @custom.
- For integrations, this would result in a pipeline name like
logs-myintegration@custom. - Without an integration, the only
@custompipeline available may belogs@custom.
If no default pipeline is detected, Streams adds a default pipeline to the data stream by updating the index templates.
If a default pipeline is detected, but it does not contain a custom pipeline, Streams adds the pipeline processor directly to the pipeline.
Streams then adds a pipeline processor to the end of that @custom pipeline. This processor definition directs matching documents to a dedicated pipeline managed by Streams called <data_stream_name>@stream.processing:
// Example processor added to the relevant @custom pipeline
{
"pipeline": {
"name": "<data_stream_name>@stream.processing",
"if": "ctx._index == '<data_stream_name>'",
"ignore_missing_pipeline": true,
"description": "Call the stream's managed pipeline - do not change this manually but instead use the Streams UI or API"
}
}
- for example, [email protected]
Streams then creates and manages the <data_stream_name>@stream.processing pipeline, adding the processors you configured in the UI.
Do not manually modify the <data_stream_name>@stream.processing pipeline created by Streams.
You can still add your own processors manually to the @custom pipeline if needed. Adding processors before the pipeline processor created by Streams may cause unexpected behavior.
- Streams does not support all processors. More processors will be added in future versions.
- The data preview simulation may not accurately reflect the changes to the existing data when editing existing processors or re-ordering them. Streams will allow proper simulations using original documents in a future version.
- Streams can't properly handle arrays. While it supports basic actions like appending or renaming, it can't access individual array elements. For classic streams, the workaround is to use the manual pipeline configuration that supports Painless scripting and all ingest processors.