Get started with KSPM
editGet started with KSPM
editThis page explains how to configure the Kubernetes Security Posture Management (KSPM) integration.
The instructions differ depending on whether you’re installing on EKS or on unmanaged clusters.
-
Install on EKS-managed clusters:
-
Install on unmanaged clusters:
Set up KSPM for Amazon EKS clusters
editName your integration and select a Kubernetes Deployment type
edit- Go to Dashboards → Cloud Posture.
- Click Add a KSPM integration.
- Read the integration’s description to understand how it works. Then, click Add Kubernetes Security Posture Management.
-
Name your integration. Use a name that matches the purpose or team of the cluster(s) you want to monitor, for example,
IT-dev-k8s-clusters. - Select EKS from the Kubernetes Deployment menu. A new section for AWS credentials will appear.
Authenticate to AWS
editThere are several options for how to provide AWS credentials:
Regardless of which option you use, you’ll need to grant the following permissions:
ecr:GetRegistryPolicy, eks:ListTagsForResource elasticloadbalancing:DescribeTags ecr-public:DescribeRegistries ecr:DescribeRegistry elasticloadbalancing:DescribeLoadBalancerPolicyTypes ecr:ListImages ecr-public:GetRepositoryPolicy elasticloadbalancing:DescribeLoadBalancerAttributes elasticloadbalancing:DescribeLoadBalancers ecr-public:DescribeRepositories eks:DescribeNodegroup ecr:DescribeImages elasticloadbalancing:DescribeLoadBalancerPolicies ecr:DescribeRepositories eks:DescribeCluster eks:ListClusters elasticloadbalancing:DescribeInstanceHealth ecr:GetRepositoryPolicy
If you are using the AWS visual editor to create and modify your IAM Policies, you can copy and paste this IAM policy JSON object:
Click to view JSON object
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "VisualEditor0",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"ecr:GetRegistryPolicy",
"eks:ListTagsForResource",
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeTags",
"ecr-public:DescribeRegistries",
"ecr:DescribeRegistry",
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeLoadBalancerPolicyTypes",
"ecr:ListImages",
"ecr-public:GetRepositoryPolicy",
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeLoadBalancerAttributes",
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeLoadBalancers",
"ecr-public:DescribeRepositories",
"eks:DescribeNodegroup",
"ecr:DescribeImages",
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeLoadBalancerPolicies",
"ecr:DescribeRepositories",
"eks:DescribeCluster",
"eks:ListClusters",
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeInstanceHealth",
"ecr:GetRepositoryPolicy"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
Option 1 - Use access keys directly
editAccess keys are long-term credentials for an IAM user or the AWS account root user. To use access keys as credentials, you need to provide the Access key ID and the Secret Access Key.
For more details, refer to AWS' Access Keys and Secret Access Keys documentation.
You must select "Programmatic access" when creating the IAM user.
Option 2 - Use temporary security credentials
editYou can configure temporary security credentials in AWS to last for a specified duration. They consist of an access key ID, a secret access key, and a security token, which is typically found using GetSessionToken.
Because temporary security credentials are short term, once they expire, you will need to generate new ones and manually update the integration’s configuration to continue collecting cloud posture data. Update the credentials before they expire to avoid data loss.
IAM users with multi-factor authentication (MFA) enabled need to submit an MFA code when calling GetSessionToken. For more details, refer to AWS' Temporary Security Credentials documentation.
You can use the AWS CLI to generate temporary credentials. For example, you could use the following command if you have MFA enabled:
`sts get-session-token --serial-number arn:aws:iam::1234:mfa/your-email@<example-url> --duration-seconds 129600 --token-code 123456`
The output from this command includes the following fields, which you should provide when configuring the KSPM integration:
-
Access key ID: The first part of the access key. -
Secret Access Key: The second part of the access key. -
Session Token: A token required when using temporary security credentials.
Option 3 - Use a shared credentials file
editIf you use different AWS credentials for different tools or applications, you can use profiles to define multiple access keys in the same configuration file. For more details refer to AWS' Shared Credentials Files documentation.
Instead of providing the Access key ID and Secret Access Key to the integration, provide the information required to locate the access keys within the shared credentials file:
-
Credential Profile Name: The profile name in the shared credentials file. -
Shared Credential File: The directory of the shared credentials file.
If you don’t provide values for all configuration fields, the integration will use these defaults:
-
If
Access key ID,Secret Access Key, andARN Roleare not provided, then the integration will check forCredential Profile Name. -
If there is no
Credential Profile Name, the default profile will be used. -
If
Shared Credential Fileis empty, the default directory will be used. -
For Linux or Unix, the shared credentials file is located at
~/.aws/credentials.
Option 4 - Use an IAM role Amazon Resource Name (ARN)
editAn IAM role Amazon Resource Name (ARN) is an IAM identity that you can create in your AWS account. You define the role’s permissions. Roles do not have standard long-term credentials such as passwords or access keys. Instead, when you assume a role, it provides you with temporary security credentials for your session. An IAM role’s ARN can be used to specify which AWS IAM role to use to generate temporary credentials.
For more details, refer to AWS' AssumeRole API documentation. Follow AWS' instructions to create an IAM user, and define the IAM role’s permissions using the JSON permissions policy above.
To use an IAM role’s ARN, you need to provide either a credential profile or access keys along with the ARN role.
The ARN Role value specifies which AWS IAM role to use for generating temporary credentials.
If ARN Role is present, the integration will check if Access key ID and Secret Access Key are present.
If not, the package will check for a Credential Profile Name.
If a Credential Profile Name is not present, the default credential profile will be used.
Finish configuring the KSPM integration for EKS
editOnce you’ve provided AWS credentials, finish configuring the KSPM integration:
- If you want to monitor Kubernetes clusters that aren’t yet enrolled in Fleet, select New Hosts under “where to add this integration”.
-
Name the Elastic Agent policy. Use a name that matches the purpose or team of the cluster(s) you want to monitor. For example,
IT-dev-k8s-clusters. -
Click Save and continue, then Add agent to your hosts. The Add agent wizard appears and provides a DaemonSet manifest
.yamlfile with pre-populated configuration information, such as theFleet IDandFleet URL.
Deploy the KSPM integration to EKS clusters
editThe Add agent wizard helps you deploy the KSPM integration on the Kubernetes clusters you wish to monitor. For each cluster:
- Download the manifest and make any necessary revisions to its configuration to suit the needs of your environment.
-
Apply the manifest using the
kubectl apply -fcommand. For example:kubectl apply -f elastic-agent-managed-kubernetes.yaml
After a few minutes, a message confirming the Elastic Agent enrollment appears, followed by a message confirming that data is incoming. You can then click View assets to see where the newly-collected configuration information appears throughout Kibana, including the Findings page and the Cloud Posture dashboard.
Set up KSPM for unmanaged Kubernetes clusters
editFollow these steps to deploy the KSPM integration to unmanaged clusters. Keep in mind credentials are NOT required for unmanaged deployments.
Configure the KSPM integration
editTo install the integration on unmanaged clusters:
- Go to Dashboards → Cloud Posture.
- Click Add a KSPM integration.
- Read the integration’s description to understand how it works. Then, click Add Kubernetes Security Posture Management.
-
Name your integration. Use a name that matches the purpose or team of the cluster(s) you want to monitor, for example,
IT-dev-k8s-clusters. - Select Unmanaged Kubernetes from the Kubernetes Deployment menu.
- If you want to monitor Kubernetes clusters that aren’t yet enrolled in Fleet, select New Hosts when choosing the Elastic Agent policy.
- Select the Elastic Agent policy where you want to add the integration.
-
Click Save and continue, then Add agent to your hosts. The Add agent wizard appears and provides a DaemonSet manifest
.yamlfile with pre-populated configuration information, such as theFleet IDandFleet URL.
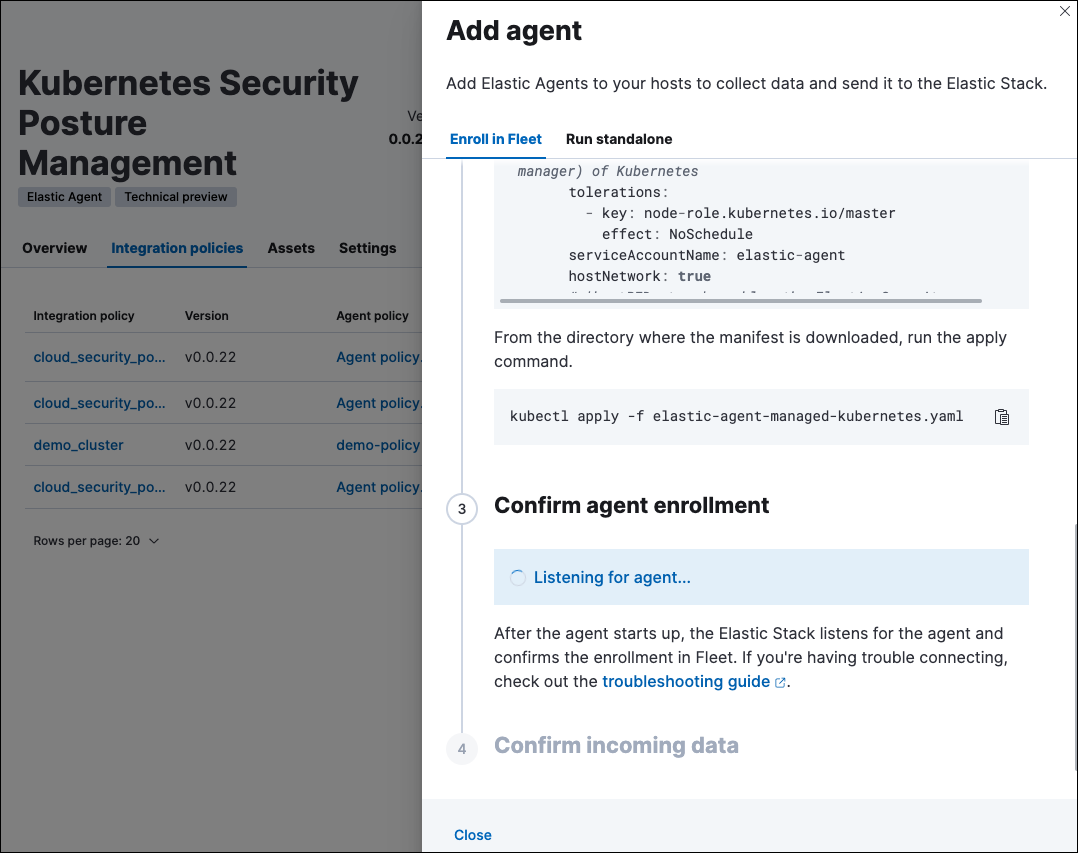
Deploy the KSPM integration to unmanaged clusters
editThe Add agent wizard helps you deploy the KSPM integration on the Kubernetes clusters you wish to monitor. To do this, for each cluster:
- Download the manifest and make any necessary revisions to its configuration to suit the needs of your environment.
-
Apply the manifest using the
kubectl apply -fcommand. For example:kubectl apply -f elastic-agent-managed-kubernetes.yaml
After a few minutes, a message confirming the Elastic Agent enrollment appears, followed by a message confirming that data is incoming. You can then click View assets to see where the newly-collected configuration information appears throughout Kibana, including the Findings page and the Cloud Posture dashboard.
Set up KSPM on ECK deployments
editTo run KSPM on an ECK deployment,
you must edit the Elastic Agent CRD and Elastic Agent Cluster-Role .yaml files.
Patch Elastic Agent
Add volumes and volumeMounts to podTemplate:
podTemplate:
spec:
containers:
- name: agent
volumeMounts:
- name: proc
mountPath: /hostfs/proc
readOnly: true
- name: cgroup
mountPath: /hostfs/sys/fs/cgroup
readOnly: true
- name: varlibdockercontainers
mountPath: /var/lib/docker/containers
readOnly: true
- name: varlog
mountPath: /var/log
readOnly: true
- name: etc-full
mountPath: /hostfs/etc
readOnly: true
- name: var-lib
mountPath: /hostfs/var/lib
readOnly: true
- name: etc-mid
mountPath: /etc/machine-id
readOnly: true
volumes:
- name: proc
hostPath:
path: /proc
- name: cgroup
hostPath:
path: /sys/fs/cgroup
- name: varlibdockercontainers
hostPath:
path: /var/lib/docker/containers
- name: varlog
hostPath:
path: /var/log
- name: etc-full
hostPath:
path: /etc
- name: var-lib
hostPath:
path: /var/lib
# Mount /etc/machine-id from the host to determine host ID
# Needed for Elastic Security integration
- name: etc-mid
hostPath:
path: /etc/machine-id
type: File
Patch RBAC
Make sure that the elastic-agent service-account has the following Role and ClusterRole:
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
namespace: default
name: elastic-agent
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: elastic-agent
namespace: default
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: elastic-agent
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: elastic-agent
labels:
k8s-app: elastic-agent
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources:
- nodes
- namespaces
- events
- pods
- services
- configmaps
- serviceaccounts
- persistentvolumes
- persistentvolumeclaims
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: ["extensions"]
resources:
- replicasets
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: ["apps"]
resources:
- statefulsets
- deployments
- replicasets
- daemonsets
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- nodes/stats
verbs:
- get
- apiGroups: [ "batch" ]
resources:
- jobs
- cronjobs
verbs: [ "get", "list", "watch" ]
- nonResourceURLs:
- "/metrics"
verbs:
- get
- apiGroups: ["rbac.authorization.k8s.io"]
resources:
- clusterrolebindings
- clusterroles
- rolebindings
- roles
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: ["policy"]
resources:
- podsecuritypolicies
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: elastic-agent
namespace: default
labels:
k8s-app: elastic-agent
rules:
- apiGroups:
- coordination.k8s.io
resources:
- leases
verbs: ["get", "create", "update"]