Connect to your own local LLM
editConnect to your own local LLM
editThis page provides instructions for setting up a connector to a large language model (LLM) of your choice using LM Studio. This allows you to use your chosen model within Elastic Security. You’ll first need to set up a reverse proxy to communicate with Elastic Security, then set up LM Studio on a server, and finally configure the connector in your Elastic deployment. Learn more about the benefits of using a local LLM.
This example uses a single server hosted in GCP to run the following components:
- LM Studio with the Mixtral-8x7b model
- A reverse proxy using Nginx to authenticate to Elastic Cloud
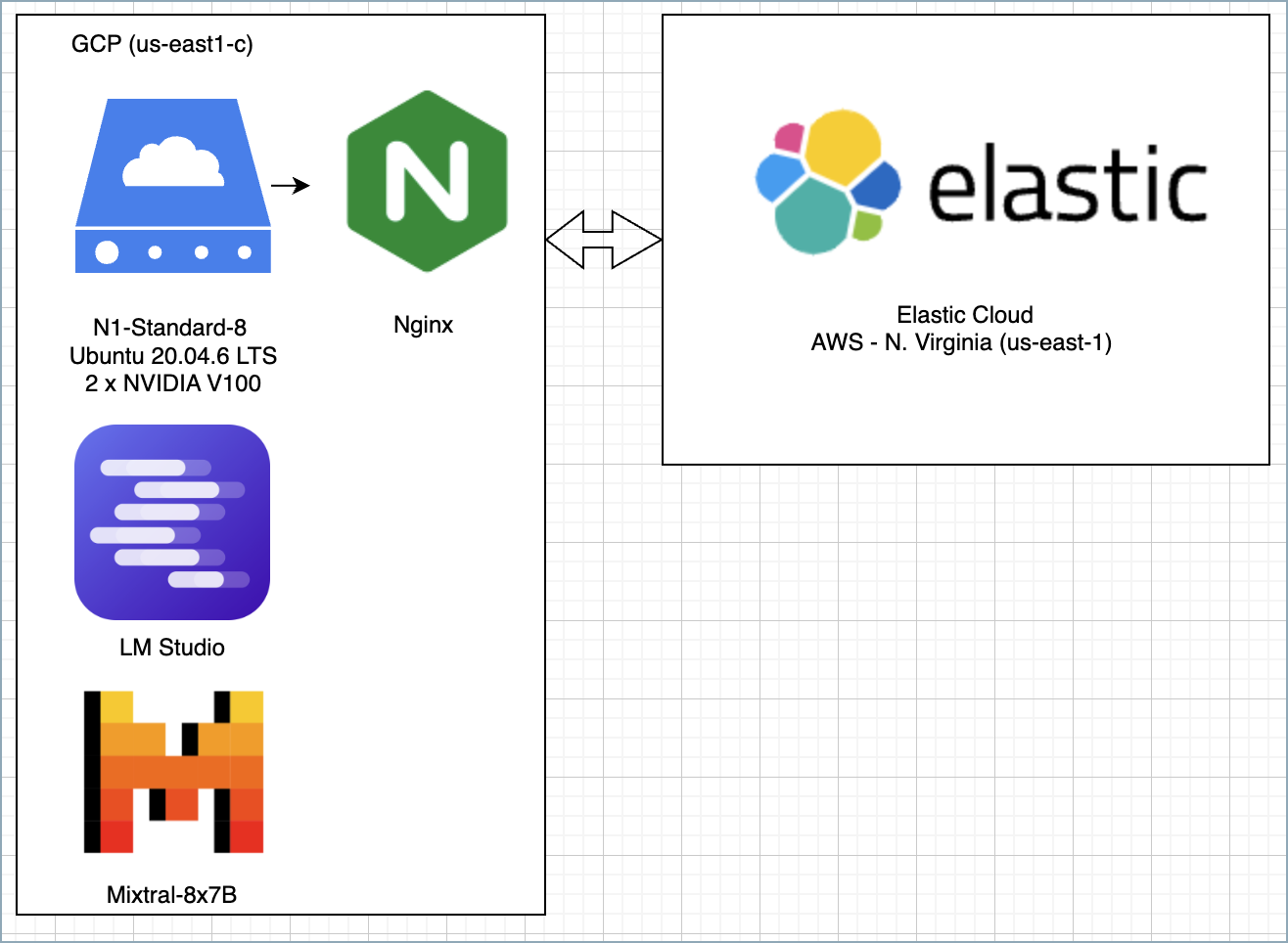
For testing, you can use alternatives to Nginx such as Azure Dev Tunnels or Ngrok, but using Nginx makes it easy to collect additional telemetry and monitor its status by using Elastic’s native Nginx integration. While this example uses cloud infrastructure, it could also be replicated locally without an internet connection.
Configure your reverse proxy
editIf your Elastic instance is on the same host as LM Studio, you can skip this step.
You need to set up a reverse proxy to enable communication between LM Studio and Elastic. For more complete instructions, refer to a guide such as this one.
The following is an example Nginx configuration file:
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name <yourdomainname.com>;
server_tokens off;
add_header x-xss-protection "1; mode=block" always;
add_header x-frame-options "SAMEORIGIN" always;
add_header X-Content-Type-Options "nosniff" always;
return 301 https://$server_name$request_uri;
}
server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
listen [::]:443 ssl http2;
server_name <yourdomainname.com>;
server_tokens off;
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/<yourdomainname.com>/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/<yourdomainname.com>/privkey.pem;
ssl_session_timeout 1d;
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:50m;
ssl_session_tickets on;
ssl_ciphers 'ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256';
ssl_protocols TLSv1.3 TLSv1.2;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload" always;
add_header x-xss-protection "1; mode=block" always;
add_header x-frame-options "SAMEORIGIN" always;
add_header X-Content-Type-Options "nosniff" always;
add_header Referrer-Policy "strict-origin-when-cross-origin" always;
ssl_stapling on;
ssl_stapling_verify on;
ssl_trusted_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/<yourdomainname.com>/fullchain.pem;
resolver 1.1.1.1;
location / {
if ($http_authorization != "Bearer <secret token>") {
return 401;
}
proxy_pass http://localhost:1234/;
}
}
If using the example configuration file above, you must replace several values: Replace <secret token> with your actual token, and keep it safe since you’ll need it to set up the Elastic Security connector. Replace <yourdomainname.com> with your actual domain name. Update the proxy_pass value at the bottom of the configuration if you decide to change the port number in LM Studio to something other than 1234.
(Optional) Set up performance monitoring for your reverse proxy
editYou can use Elastic’s Nginx integration to monitor performance and populate monitoring dashboards in the Elastic Security app.
Configure LM Studio and download a model
editFirst, install LM Studio. LM Studio supports the OpenAI SDK, which makes it compatible with Elastic’s OpenAI connector, allowing you to connect to any model available in the LM Studio marketplace.
One current limitation of LM Studio is that when it is installed on a server, you must launch the application using its GUI before doing so using the CLI. For example, by using Chrome RDP with an X Window System. After you’ve opened the application the first time using the GUI, you can start it by using sudo lms server start in the CLI.
Once you’ve launched LM Studio:
- Go to LM Studio’s Search window.
-
Search for an LLM (for example,
Mixtral-8x7B-instruct). Your chosen model must includeinstructin its name in order to work with Elastic. -
Filter your search for "Compatibility Guess" to optimize results for your hardware. Results will be color coded:
- Green means "Full GPU offload possible", which yields the best results.
- Blue means "Partial GPU offload possible", which may work.
- Red for "Likely too large for this machine", which typically will not work.
- Download one or more models.
For security reasons, before downloading a model, verify that it is from a trusted source. It can be helpful to review community feedback on the model (for example using a site like Hugging Face).
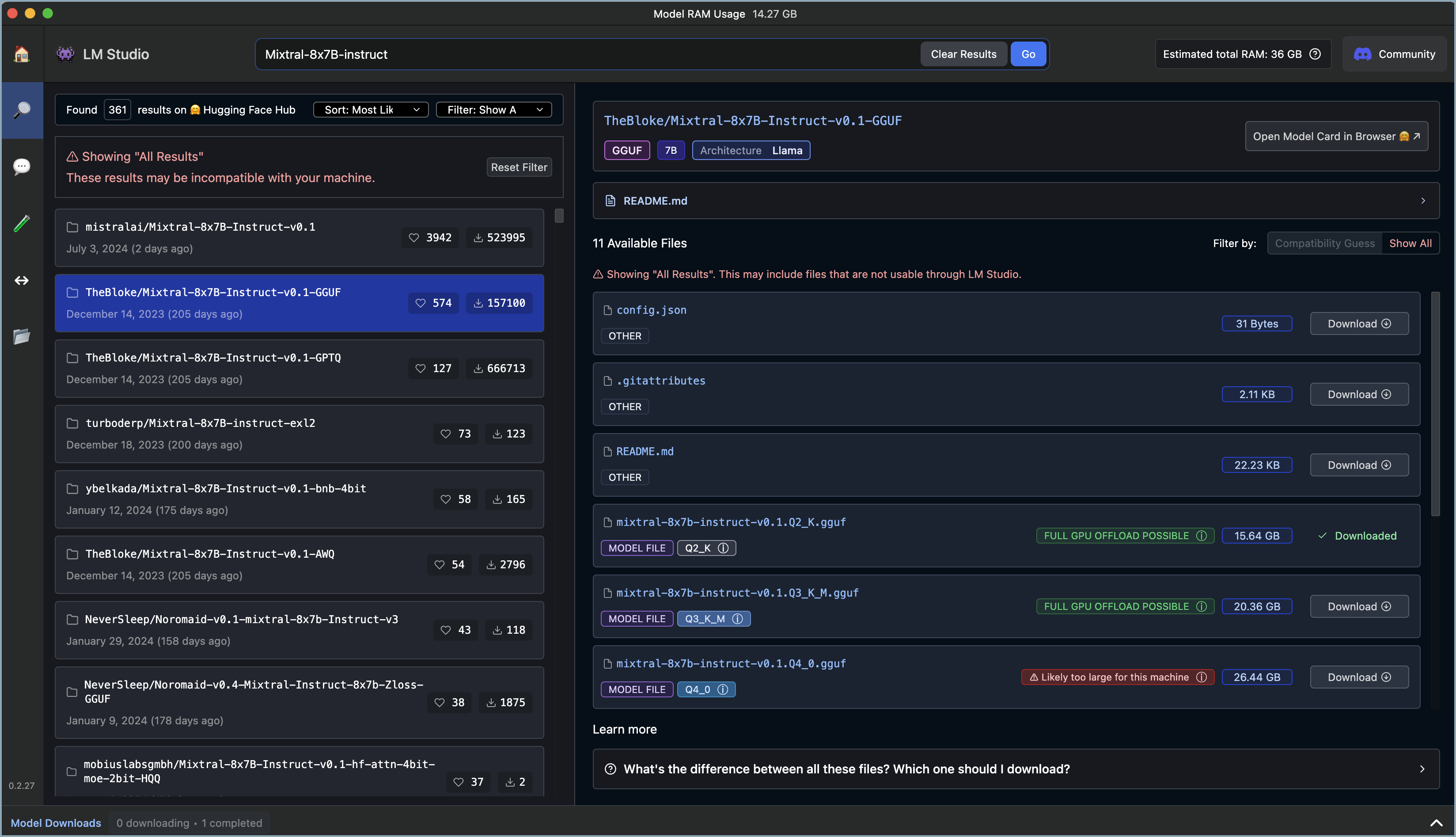
In this example we used TheBloke/Mixtral-8x7B-Instruct-v0.1.Q3_K_M.gguf. It has 46.7B total parameters, a 32,000 token context window, and uses GGUF quanitization. For more information about model names and format information, refer to the following table.
| Model Name | Parameter Size | Tokens/Context Window | Quantization Format |
|---|---|---|---|
Name of model, sometimes with a version number. |
LLMs are often compared by their number of parameters — higher numbers mean more powerful models. |
Tokens are small chunks of input information. Tokens do not necessarily correspond to characters. You can use Tokenizer to see how many tokens a given prompt might contain. |
Quantization reduces overall parameters and helps the model to run faster, but reduces accuracy. |
Examples: Llama, Mistral, Phi-3, Falcon. |
The number of parameters is a measure of the size and the complexity of the model. The more parameters a model has, the more data it can process, learn from, generate, and predict. |
The context window defines how much information the model can process at once. If the number of input tokens exceeds this limit, input gets truncated. |
Specific formats for quantization vary, most models now support GPU rather than CPU offloading. |
Load a model in LM Studio
editAfter downloading a model, load it in LM Studio using the GUI or LM Studio’s CLI tool.
Option 1: load a model using the CLI (Recommended)
editIt is a best practice to download models from the marketplace using the GUI, and then load or unload them using the CLI. The GUI allows you to search for models, whereas the CLI only allows you to import specific paths, but the CLI provides a good interface for loading and unloading.
Use the following commands in your CLI:
-
Verify LM Studio is installed:
lms -
Check LM Studio’s status:
lms status -
List all downloaded models:
lms ls -
Load a model:
lms load
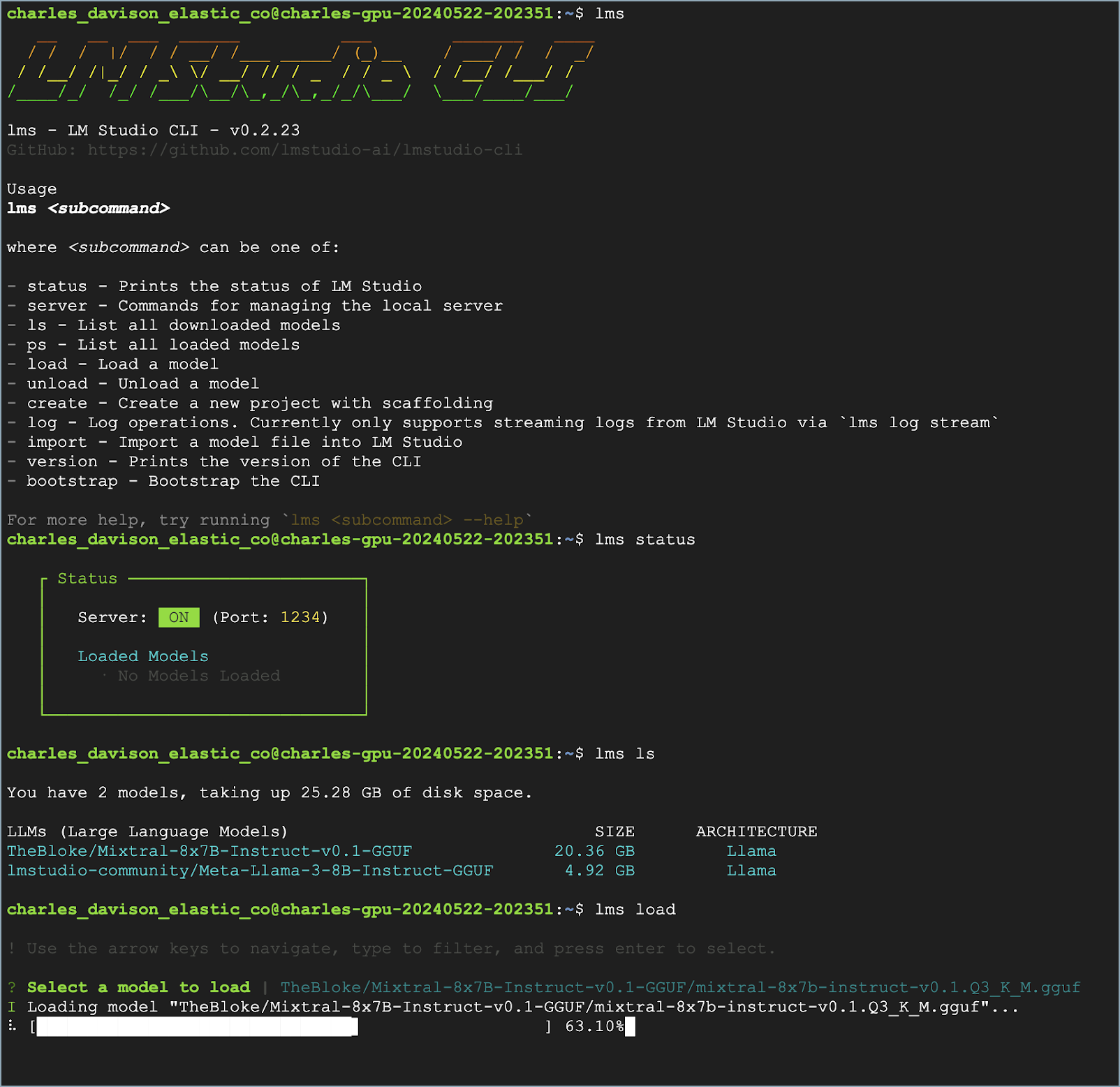
After the model loads, you should see a Model loaded successfully message in the CLI.
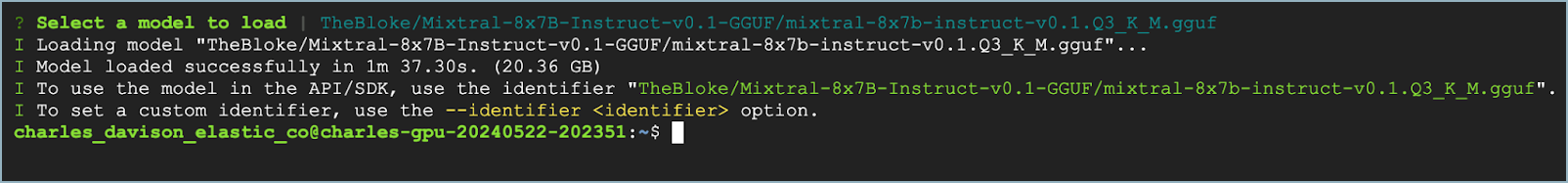
To verify which model is loaded, use the lms ps command.
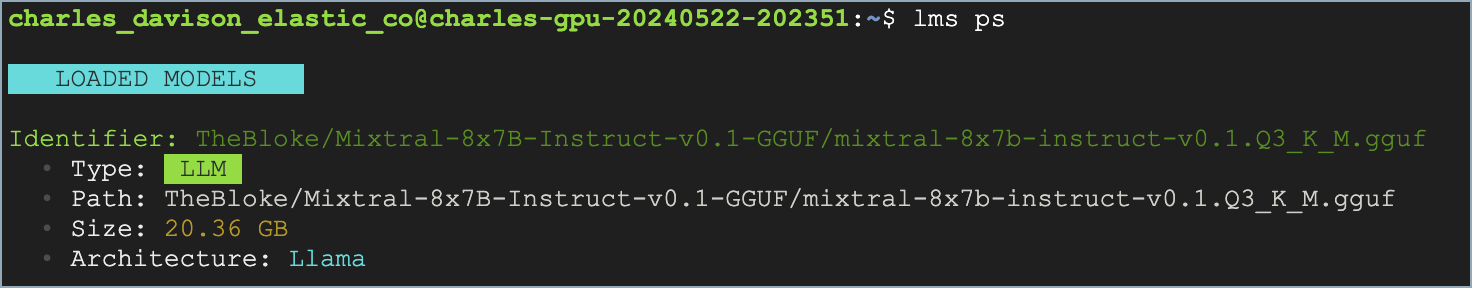
If your model uses NVIDIA drivers, you can check the GPU performance with the sudo nvidia-smi command.
Option 2: load a model using the GUI
editRefer to the following video to see how to load a model using LM Studio’s GUI. You can change the port setting, which is referenced in the Nginx configuration file. Note that the GPU offload was set to Max.

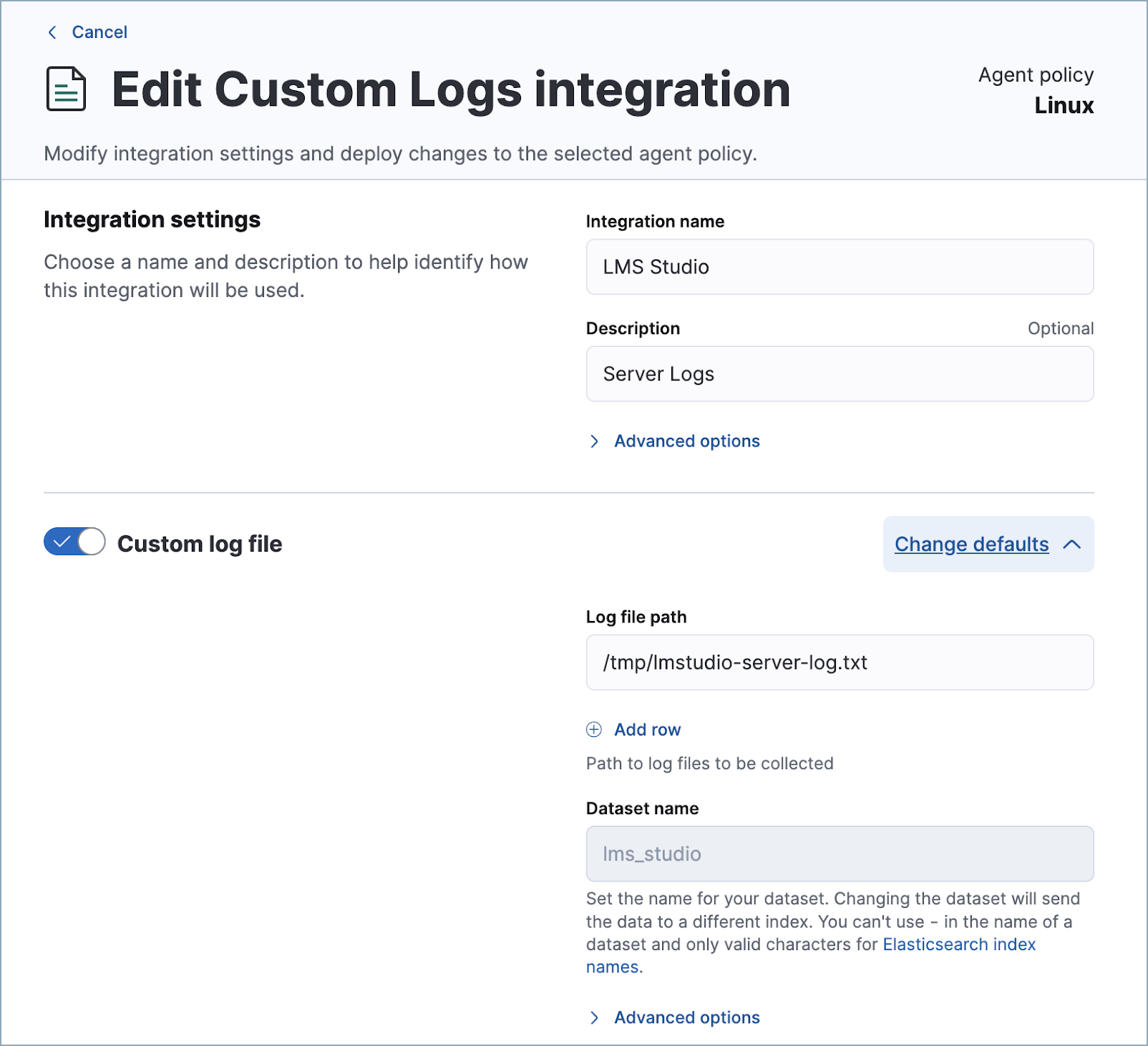
(Optional) Collect logs using Elastic’s Custom Logs integration
editYou can monitor the performance of the host running LM Studio using Elastic’s Custom Logs integration. This can also help with troubleshooting. Note that the default path for LM Studio logs is /tmp/lmstudio-server-log.txt, as in the following screenshot:
Configure the connector in your Elastic deployment
editFinally, configure the connector:
- Log in to your Elastic deployment.
- Find the Connectors page in the navigation menu or use the global search field. Then click Create Connector, and select OpenAI. The OpenAI connector enables this use case because LM Studio uses the OpenAI SDK.
- Name your connector to help keep track of the model version you are using.
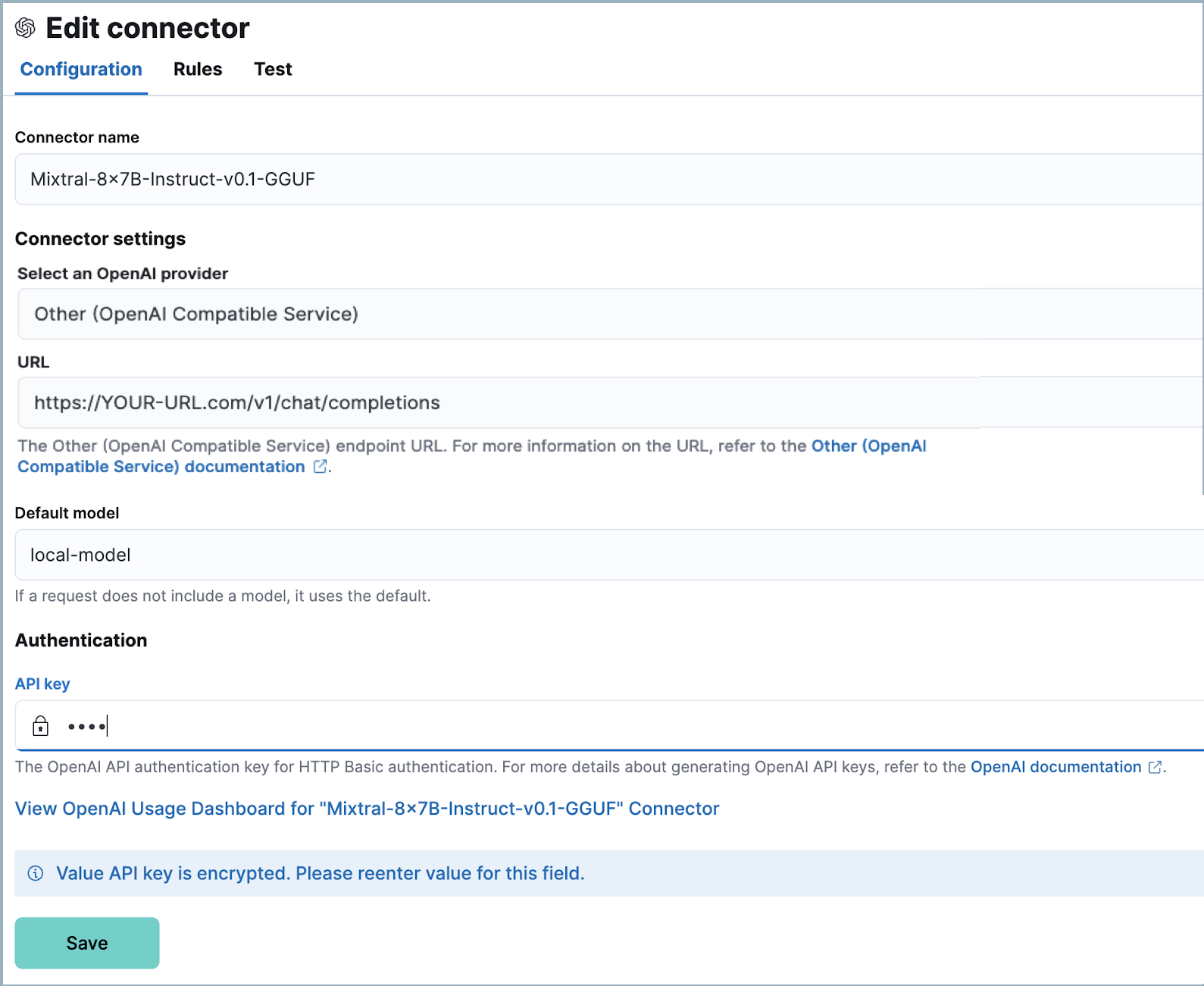
- Under Select an OpenAI provider, select Other (OpenAI Compatible Service).
-
Under URL, enter the domain name specified in your Nginx configuration file, followed by
/v1/chat/completions. -
Under Default model, enter
local-model. - Under API key, enter the secret token specified in your Nginx configuration file.
- Click Save.
Setup is now complete. You can use the model you’ve loaded in LM Studio to power Elastic’s generative AI features. You can test a variety of models as you interact with AI Assistant to see what works best without having to update your connector.
While local models work well for AI Assistant, we recommend you use one of these models for interacting with Attack discovery. As local models become more performant over time, this is likely to change.