Benchmarks
editBenchmarks
editThe Benchmarks page lets you view the cloud security posture (CSP) benchmark rules for the Cloud security posture management (CSPM) and Kubernetes security posture management (KSPM) integrations.
What are benchmark rules?
editBenchmark rules are used by the CSPM and KSPM integrations to identify configuration risks in your cloud infrastructure. Benchmark rules are based on the Center for Internet Security’s (CIS) secure configuration benchmarks.
Each benchmark rule checks to see if a specific type of resource is configured according to a CIS Benchmark. The names of rules describe what they check, for example:
-
Ensure Kubernetes Secrets are encrypted using Customer Master Keys (CMKs) managed in AWS KMS -
Ensure the default namespace is not in use -
Ensure IAM policies that allow full "*:*" administrative privileges are not attached -
Ensure the default namespace is not in use
When benchmark rules are evaluated, the resulting findings data appears on the Cloud Security Posture dashboard.
Benchmark rules are not editable.
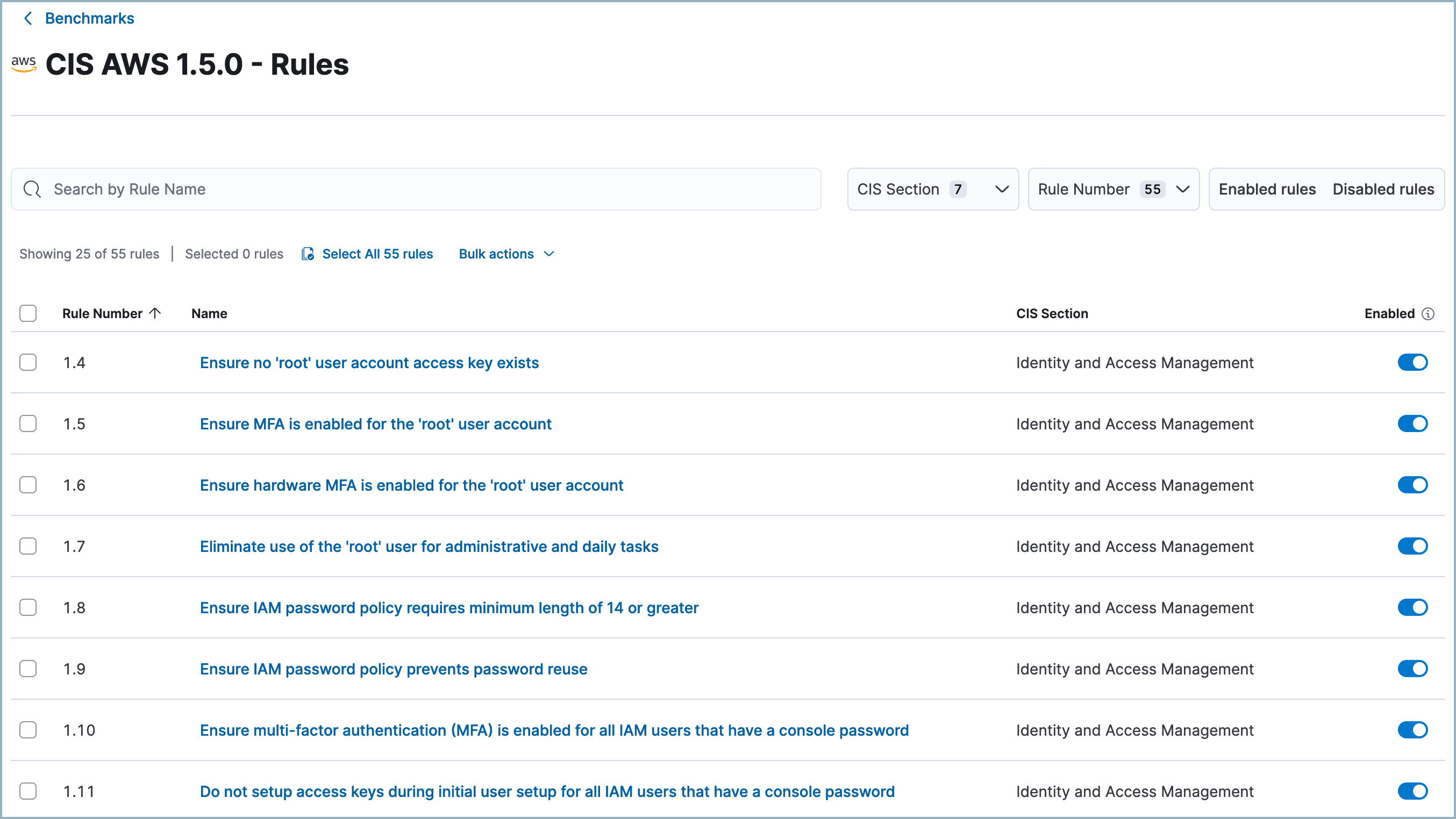
Review your benchmarks
editFind Benchmarks in the navigation menu or use the global search field. From there, you can click a benchmark’s name to view the benchmark rules associated with it. You can click a benchmark rule’s name to see details including information about how to remediate it, and related links.
Benchmark rules are enabled by default, but you can disable some of them — at the benchmark level — to suit your environment. This means for example that if you have two integrations using the CIS AWS benchmark, disabling a rule for that benchmark affects both integrations. To enable or disable a rule, use the Enabled toggle on the right of the rules table.
Disabling a benchmark rule automatically disables any associated detection rules and alerts. Re-enabling a benchmark rule does not automatically re-enable them.
How benchmark rules work
edit- When a security posture management integration is deployed, and every four hours after that, Elastic Agent fetches relevant cloud resources.
- After resources are fetched, they are evaluated against all applicable enabled benchmark rules.
-
Finding values of
passorfailindicate whether the standards defined by benchmark rules were met.