WARNING: Version 6.2 of Kibana has passed its EOL date.
This documentation is no longer being maintained and may be removed. If you are running this version, we strongly advise you to upgrade. For the latest information, see the current release documentation.
Graphing Connections in Your Data
editGraphing Connections in Your Data
editThe X-Pack graph capabilities enable you to discover how items in an Elasticsearch index are related. You can explore the connections between indexed terms and see which connections are the most meaningful. This can be useful in a variety of applications, from fraud detection to recommendation engines.
For example, graph exploration could help you uncover website vulnerabilities that hackers are targeting so you can harden your website. Or, you might provide graph-based personalized recommendations to your e-commerce customers.
X-Pack provides a simple, yet powerful graph exploration API, and an interactive graph visualization tool for Kibana. Both work out of the box with existing Elasticsearch indices—you don’t need to store any additional data to use the X-Pack graph features.
How Graphs Work
editThe Graph API provides an alternative way to extract and summarize information about the documents and terms in your Elasticsearch index. A graph is really just a network of related items. In our case, this means a network of related terms in the index.
The terms you want to include in the graph are called vertices. The relationship between any two vertices is a connection. The connection summarizes the documents that contain both vertices' terms.
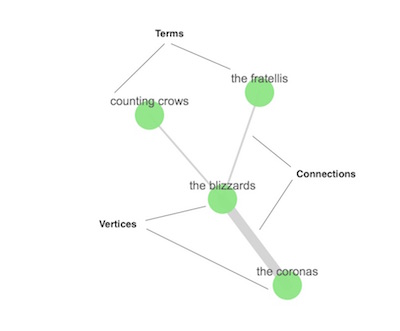
If you’re into graph theory, you might know vertices and connections as nodes and edges. They’re the same thing, we just want to use terminology that makes sense to people who aren’t graph geeks and avoid any confusion with the nodes in an Elasticsearch cluster.
The graph vertices are simply the terms that you’ve already indexed. The connections are derived on the fly using Elasticsearch aggregations. To identify the most meaningful connections, the Graph API leverages Elasticsearch relevance scoring. The same data structures and relevance ranking tools built into Elasticsearch to support text searches enable the Graph API to separate useful signals from the noise that is typical of most connected data.
This foundation lets you easily answer questions like:
- What are the shared behaviors of people trying to hack my website?
- If users bought this type of gardening glove, what other products might they be interested in?
- Which people on Stack Overflow have expertise in both Hadoop-related technologies and Python-related tech?
But what about performance, you ask? The Elasticsearch aggregation framework enables the Graph API to quickly summarize millions of documents as a single super-connection. Instead of retrieving every banking transaction between accounts A and B, it derives a single connection that represents that relationship. And, of course, this summarization process works across multi-node clusters and scales with your Elasticsearch deployment. Advanced options let you control how your data is sampled and summarized. You can also set timeouts to prevent graph queries from adversely affecting the cluster.