Set up Enterprise Search with LDAP user authentication
editSet up Enterprise Search with LDAP user authentication
edit
This feature is not available for all Elastic subscription levels. Refer to the subscriptions pages for Elastic Cloud and Elastic Stack. To change your subscription level or start a trial, see Elastic subscription.
The following documentation describes the process of configuring Elasticsearch and Kibana:
Within your Enterprise Search configuration settings, make sure that:
-
kibana.hostis set -
kibana.external_urlis set -
any
auth.sourceconfigurations are removed.
Configure Enterprise Search role mappings for LDAP users
editWhen a user is logged in to Enterprise Search in Kibana via LDAP, the following metadata properties would be populated:
-
ldap_dn: user’s distinguished name -
ldap_groups: the distinguished name of each of the groups that were resolved for the user.
Based on those metadata fields, it is possible to create role mappings that apply to groups of users. For example, members of the group called Admins might get admin permissions to Workplace Search:
PUT _security/role_mapping/workplace_search_admin_ldap
{
"roles": ["enterprise-search-workplace-search-admin"],
"rules" : {
"field" : {
"groups" : "cn=Admins,ou=Groups,dc=example,dc=org"
}
},
"enabled": true
}
While members of the group called Users would get user permissions:
PUT _security/role_mapping/workplace_search_user_ldap
{
"roles": ["enterprise-search-workplace-search-user"],
"rules" : {
"field" : {
"groups" : "cn=Users,ou=Groups,dc=example,dc=org"
}
},
"enabled": true
}
Users can also be mapped in Users and Roles in Enterprise Search UI in Kibana:
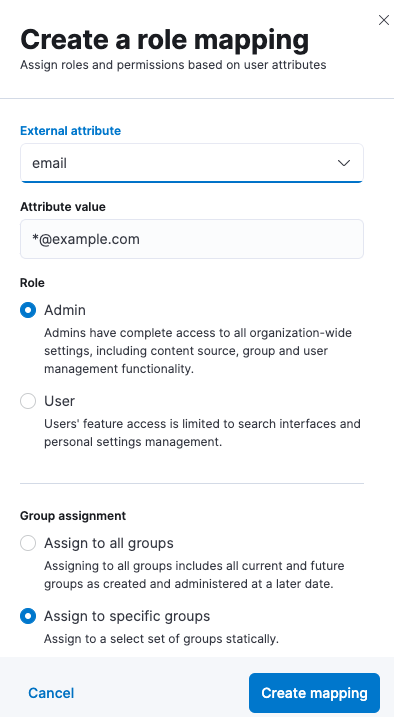
Mapping can use common Elasticsearch user attributes, such as username and email, but also anything provided in metadata that is returned by a LDAP provider. Here is an example of metadata:
{
"ldap_dn" : "cn=adminuser,dc=example,dc=org",
"mail" : "[email protected]",
"displayName" : "Enterprise Search Admin User",
"ldap_groups" : [
"cn=Admins,ou=Groups,dc=example,dc=org"
],
"cn" : "adminuser"
}
In Elasticsearch, the LDAP realm that provided this metadata would be configured as follows:
xpack:
security:
authc:
realms:
ldap:
ldap1:
order: 1
url: "ldap://ldap-server.example.org"
bind_dn: "cn=admin,dc=example,dc=org"
user_search:
base_dn: "dc=example,dc=org"
filter: "(cn={0})"
group_search:
base_dn: "ou=Groups,dc=example,dc=org"
unmapped_groups_as_roles: false
metadata:
- cn
- mail
- displayName
For more information about configuring metadata returned by an LDAP realm, see User metadata in LDAP realms.