Manage seasonal time changes smoothly in Elasticsearch
New daylight saving time calendars for Elasticsearch anomaly detection

Twice a year in the spring and fall, many countries change their clocks to make better use of the daylight. These clock adjustments not only bring a feeling of jet lag and "sleepy Monday" but also a burst of false positive alerts from anomaly detection jobs. These false positives happen because Elastic machine learning needs a few days to adapt to the new data patterns.
Starting with Elasticsearch 8.16 — and now available in our Elastic Cloud Serverless offering — you can instruct the anomaly detection job to adjust its time when you change your clock. No more pesky false positives!
How to create a new daylight saving time calendar
To make sure anomaly detection jobs adjust correctly for daylight saving time (DST), you need to create a DST calendar for your time zone and associate it with your jobs or job groups.
1. Create a new DST calendar in Kibana: Go to Machine Learning > Anomaly Detection > Settings. You will see an option to create a DST calendar in addition to the regular calendar.
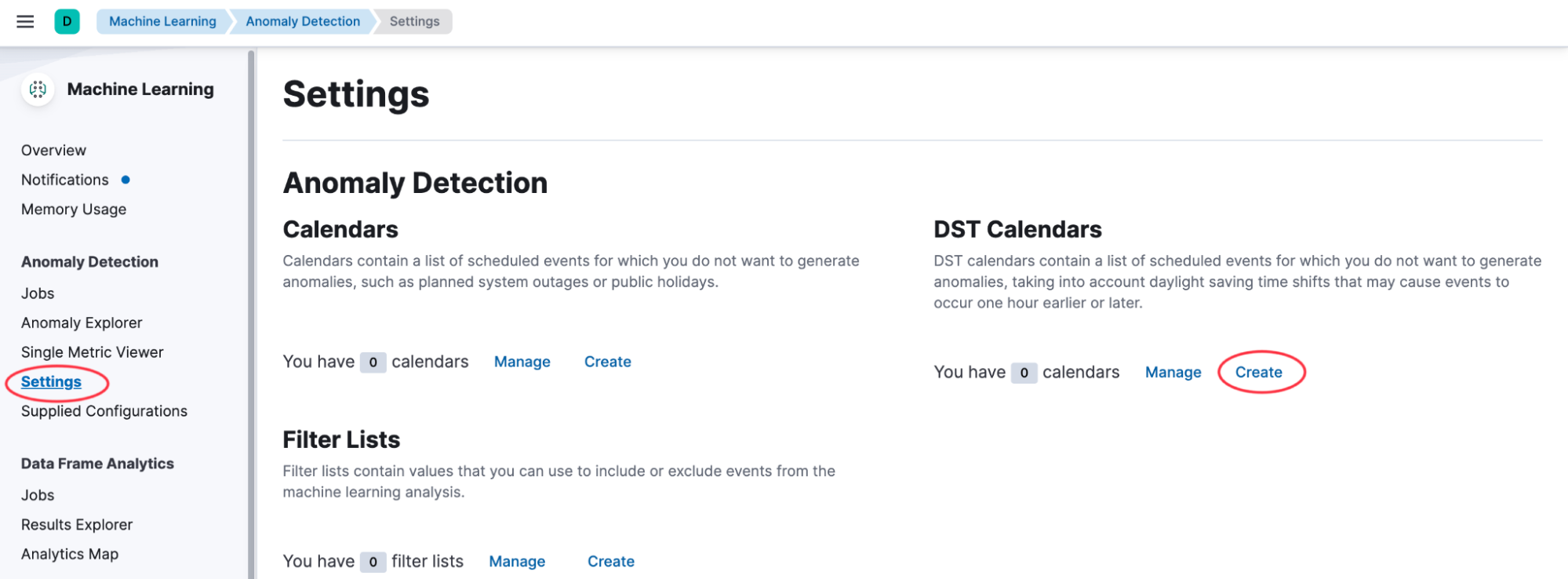
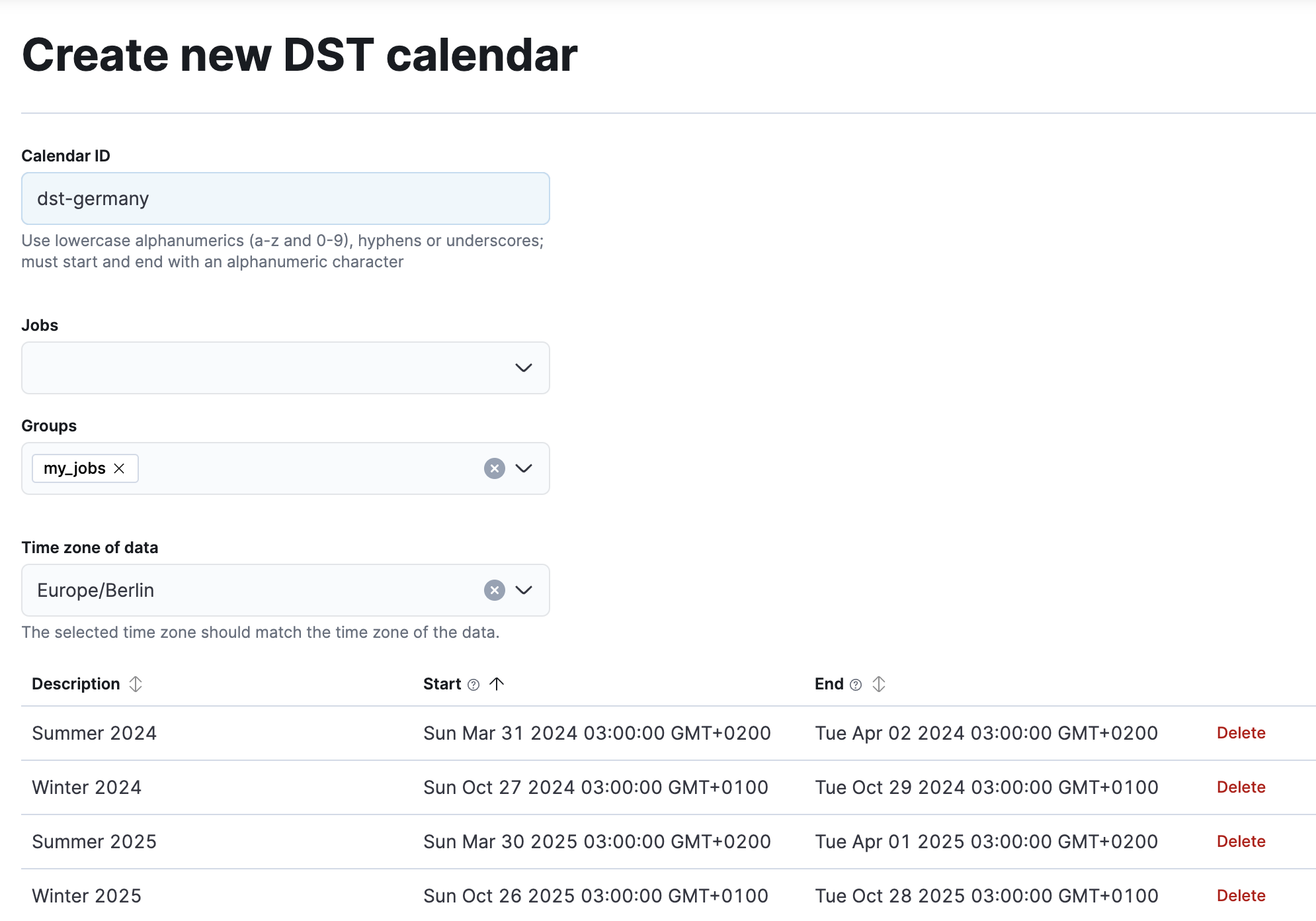
2. Select the time zone: In the DST calendar wizard, select the time zone of your data. This may not be the same time zone that you are in, but it must be the time zone from which the data in the index originated.
Different countries and time zones have different rules for DST. The wizard will automatically generate calendar events for the selected time zone that force a time shift for the associated jobs.
3. Associate the jobs or job groups: Calendars can be linked to existing jobs by selecting them here. If you have multiple jobs that require the same DST calendar, you can put them in a common group and assign the calendar to that group.
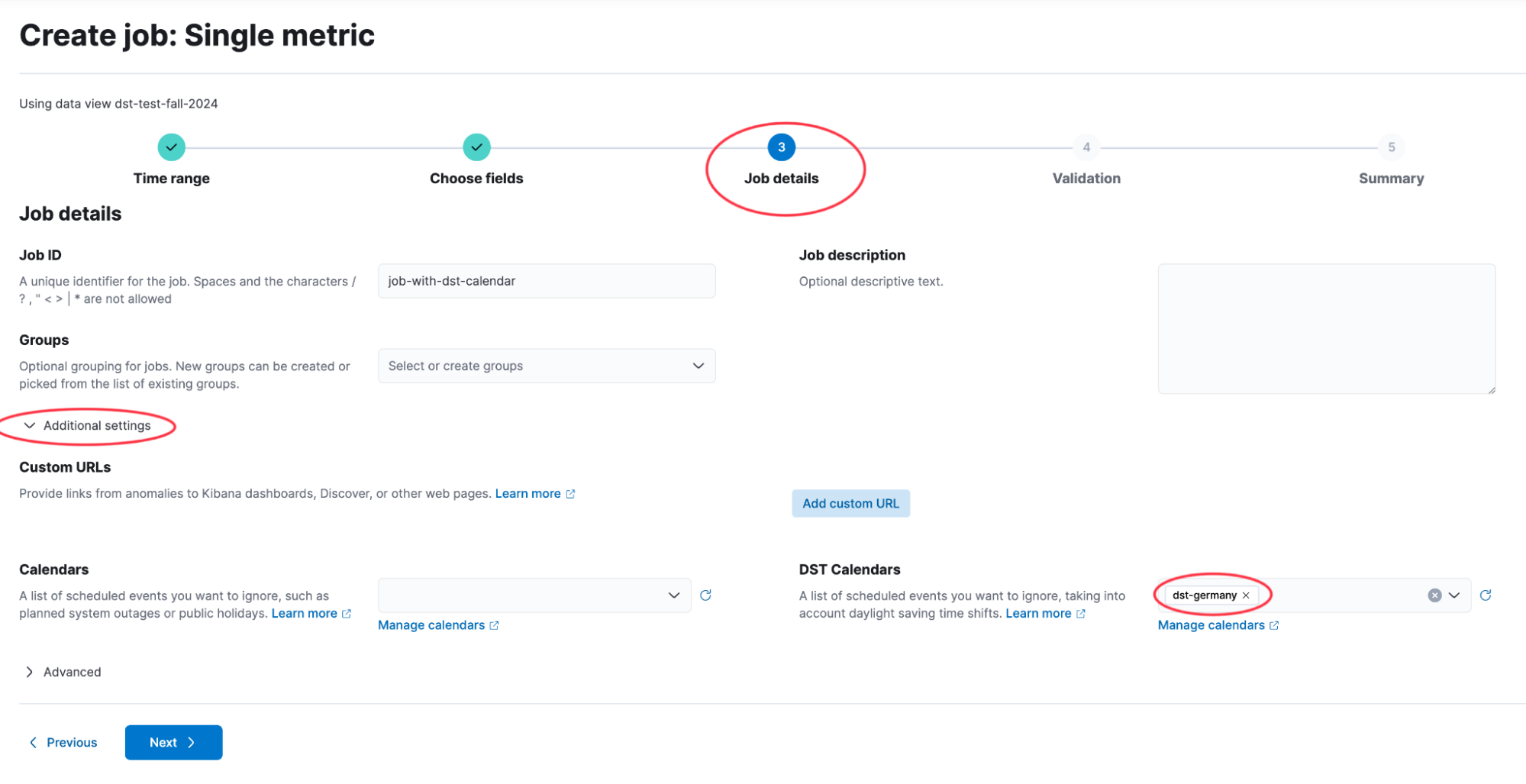
4. Associate new jobs with the DST calendar: Rather than assigning a DST calendar to an existing job, you can assign it during the job’s creation in the new job wizard.
In the Advanced Settings section of the new job wizard, you can either select an existing DST calendar or place the job in a group that has already been assigned to a DST calendar.
Managing multiple time zones with DST calendars
If you are in a country with multiple time zones and complex DST rules, such as Australia or the US, you may need to create several calendars and multiple anomaly detection jobs. You can use filter queries in the data feed configuration to route data from different time zones to different jobs.
For example, if you need to handle data in Australia, you would need to create three jobs:
Regions shifting time by 1 hour: Australian Capital Territory, Jervis Bay Territory, New South Wales (except Lord Howe Island), Norfolk Island, South Australia, Tasmania, and Victoria
Region shifting time by 30 minutes: Lord Howe Island
Regions not shifting time: Western Australia, Queensland, and Northern Territory
Try out the new DST calendar
The new DST calendar functionality helps you effectively manage daylight saving time changes and prevent false positives in your anomaly detection jobs. This feature is already available in Elastic Cloud Serverless and will be included in Elasticsearch 8.16.
Ready to try out the new DST calendar? Sign up for Elastic Cloud Serverless today to take advantage of the latest features, hassle-free operations, and seamless scaling.
The release and timing of any features or functionality described in this post remain at Elastic's sole discretion. Any features or functionality not currently available may not be delivered on time or at all.